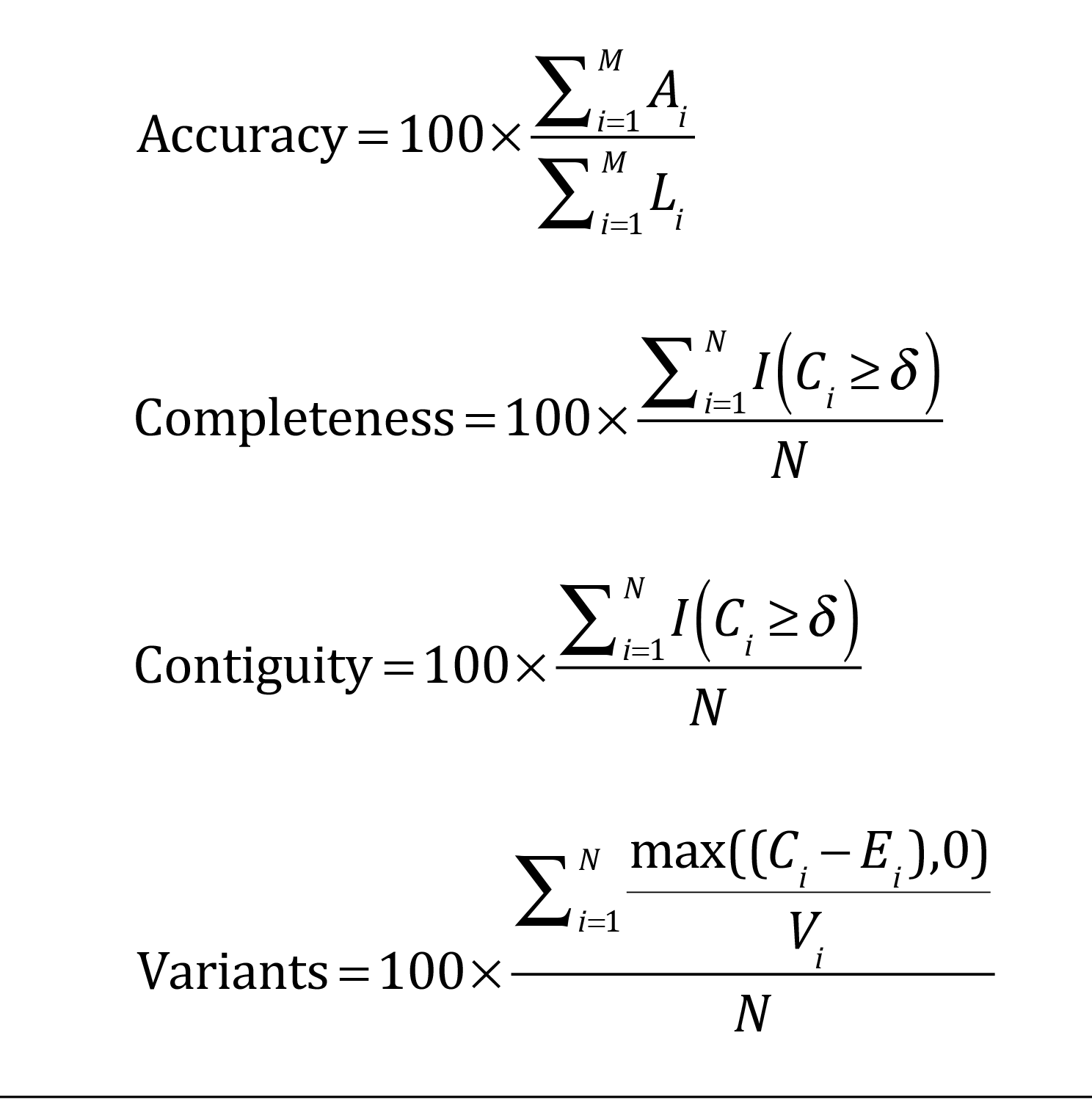
Li = length of alignment between a reference and an assembled transcript, Ti; Ai = number of correct bases in Ti; M = number of best alignments between assembled and reference transcripts; N = number of reference transcripts; I = the indicator function; Ci = percentage of a reference transcript covered by Ti, δ is a user-defined percentage (Martin and Wang, 2011).
Quality Control: Transcriptome Assembly
Metrics developed by Martin and Wang (2011) are summarized below; corresponding equations are shown in the figure. To calculate the metrics, a set of reference transcripts must be expressed in the sample. The reference set should ideally come from the transcriptome of interest and contain transcripts of different lengths and expression levels.
- Accuracy is the percentage of the correctly assembled bases estimated using the set of expressed reference transcripts.
- Completeness is the percentage of expressed reference transcripts covered by all the assembled all the assembled transcripts.
- Contiguity is the percentage of expressed reference transcripts covered by a sing, longest-assembled transcript.
- Chimerism is the percentage of chimeras that occur due to misassemblies among all of the assembled transcripts. A chimera is an assembled transcript that contains non-repetitive parts from two or more reference genes. Misassembled chimeric transcripts will have a low number of reads spanning the chimeric junction relative to the number of reads spanning other segments.
- Variant resolution is the percentage of transcript variants assembled within the reference set.