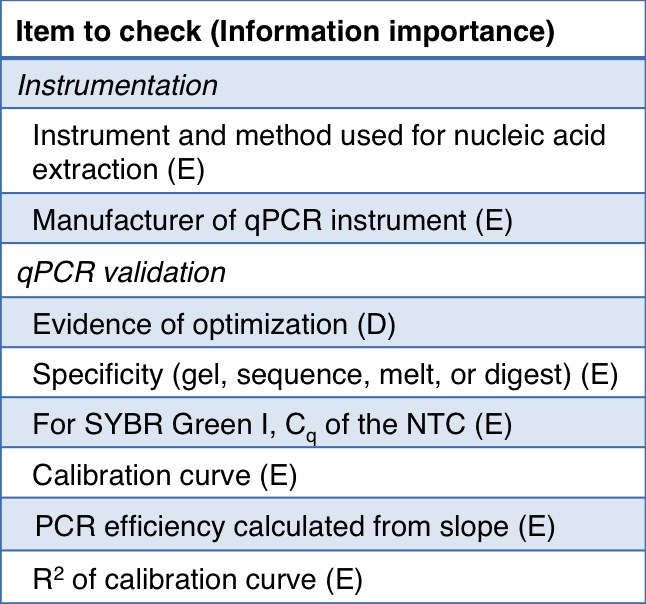
MIQE guidelines excerpt from Bustin et al. (2009). Information importance: E = essential; D = desirable. Cq = threshold cycle (CT); NTC = no template control.
Quality Control: Instrumentation and PCR validation
- qPCR equipment should be checked regularly (for more information see Life Technologies, 2012)
- With age, the excitation source (e.g., halogen lamp or LED) and the emission detector (e.g., photodiode) may lead to variable excitation strength or emission sensitivity across a plate. A passive reference dye may be used to correct for this.
- Calibration curves should be generated as part of a maintenance regimen and prior to using new dyes.
- PCR validation
- Standard calibration curves should be repeated over time to maintain data quality.
- Determine whether the efficiency is within the acceptable range of 90 to 110%.
- The R2 value is a measure of replicate reproducibility.
- Individual reaction efficiencies should be similar.
- Melting curve analysis applies to methods that use a fluorescent dye that remains associated with the amplicon (e.g., SYBR® Green I).
- The first derivative of a melting curve (-d(RFU)/dT) provides a better graph for analysis.
- All amplicon DNA should melt at the same temperature; primer dimers melt at a lower temperature.
- Blanks that show a peak indicate the presence of DNA.